Joint Economic Forecast for Germany: Pandemic delays upswing – Demography slows growth
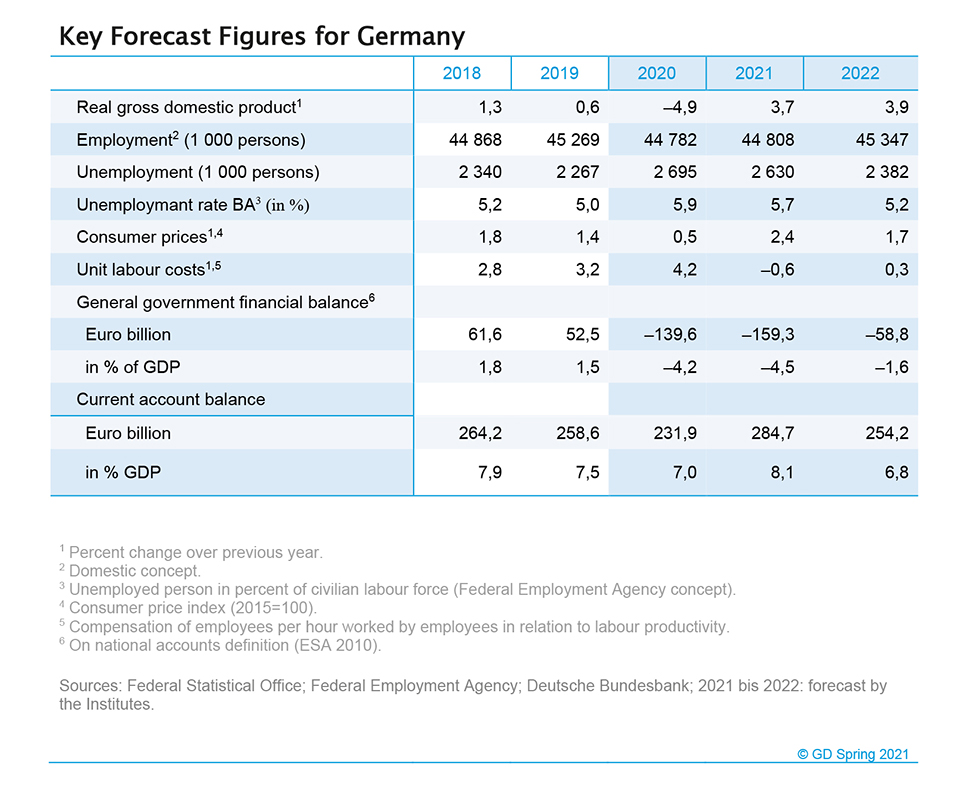
In their spring report, the leading economic research institutes - amongst them the ifo Institute in cooperation with the KOF Swiss Economic Institute - forecast an increase in gross domestic product of 3.7 percent in the current year and 3.9 percent in 2022. The renewed shutdown is delaying the economic recovery, but as soon as the risks of infection, particularly from vaccination, have been averted, a strong recovery will begin.

“Economic output is likely to have dropped by 1.8 percent in the first quarter due to the continuing shutdown,” said Torsten Schmidt, Chief Economist at RWI – Leibniz Institute for Economic Research. The new wave of infections and the associated containment measures lead to the downward revision of the forecast for 2021 by 1 percentage point compared to the fall forecast 2020.
In their forecast, the institutes assume that the current shutdown will continue for the time being and that the most recent easing measures will be largely reversed. Further easing is not expected until the middle of the second quarter, with restrictions probably lifted by the end of the third quarter. “We expect a vigorous expansion of economic activities as the measures are gradually lifted over the course of the six months through the summer, especially in the services sector that was particularly affected by the pandemic,” Schmidt added.
Employment is expected to rise
Employment is also likely to gain momentum in view of the expected easing of restrictions. On average, employment is expected to rise by 26,000 over 2021. The rise is estimated at 539,000 over the coming year, with pre-crisis levels being reached in the first half-year. Unemployment levels are also expected to drop more sharply as the infection control measures are gradually lifted.
Public budgets are expected to show a deficit of €159 billion in 2021, slightly higher than in the previous year. Tax revenues are already rising again due to the economic situation. However, spending on vaccinations and tests is causing social benefits in kind to rise sharply. Moreover, government investment is likely to continue expanding, especially due to the funds available in investment programmes. In relation to GDP, the general government budget deficit is expected to remain roughly the same at 4.5 percent in 2021 and to drop significantly to 1.6 percent in 2022.
The development of the pandemic remains a downside risk
The coronavirus pandemic is leaving its mark on production potential as well. Current forecasts suggest that between 2020 and 2024, it is likely to be on average around 1.1 percent below the levels originally estimated prior to the Corona crisis. In addition, there are already signs that Germany is facing a far-reaching demographic transition in the years ahead. The total workforce will shrink as the baby boomers reach retirement age, accompanied by a sharp rise in the proportion of older people. This will have serious consequences for growth potential: projections indicate that the rate of growth potential is expected to decline by around one percentage point by 2030.
The further development of the pandemic remains the most significant downside risk to the outlook. Bottlenecks and delays may still occur in the delivery of vaccines and tests. Moreover, the emergence of new virus mutations might erode the effectiveness of vaccines, potentially halting the opening process and once again causing setbacks in the economic recovery.
The Joint Economic Forecast was prepared by the German Institute for Economic Research (DIW Berlin), the ifo Institute (Munich) in cooperation with the KOF Economic Institute (Zurich), the Kiel Institute (IfW Kiel), the Halle Institute for Economic Research (IWH), and RWI (Essen).
The complete report is external page here available (in German).
Contact
KOF Konjunkturforschungsstelle
Leonhardstrasse 21
8092
Zürich
Switzerland