Review
In 2023 we celebrated KOF’s 85th anniversary. This occasion marked 85 years of evidence-based economic research at the heart of the business community.

Research highlights
Surveys and forecasts are part of our DNA
A key plank of our activities ever since KOF was founded in 1938 is our Business Tendency Surveys. With more than 11,000 firms participating in these surveys, KOF has one of the largest voluntary panels in Switzerland. As such questionnaires are also relevant for research purposes, a team from KOF, EPFL and the University of Lausanne began to set up a panel of firms for research surveys. This project is being funded by the MTEC Foundation and the E4S Foundation.
The first survey has already been conducted and asked participants how important energy costs are for decision-makers in Switzerland. The survey revealed that some firms are heavily reliant on energy prices and that most businesses are highly interested in the associated costs. As energy price changes vary from one firm to another, the promotion of a fairly priced energy cost insurance scheme might be one option.

We focus not only on constantly supporting such panels but also on enhancing the quality of data in our Business Tendency Surveys. We are continually improving the quality of this data as well as the way in which data is supplied to respondents, institutions and clients. Since last year, for example, we have been providing customers with the responses to some questions in the manufacturing sector once a month instead of quarterly as in the past. This data includes firms’ expectations about their exports, sales prices or the overall performance of their business. This ensures that our Business Tendency Surveys give an even more accurate picture of the economic situation.
However, KOF does not only conduct surveys on the economic situation. Further significant questionnaires are its surveys on firms’ investment plans and innovation activities. The semi-annual Investment Survey has been expanded to include questions on aspects of climate change and the effects of the weather. This is modelled on the European Investment Bank, which asks similar questions in its annual investment survey. These questions were first included in the spring survey of 2023 and the findings were placed in a European context.
Last year saw the launch of a new wave of questionnaires as part of KOF’s Innovation Survey, which is conducted every two years on behalf of Switzerland’s State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI). As innovation is the driver of economic growth and requires the right conditions, this survey has formed one of the bases for political decision-making since the 1990s. The findings of the latest surveys will be published in the autumn of 2024.
New models used to estimate the performance of the Swiss economy

In addition to surveys, forecasts form the second key plank of KOF’s activities. High-quality estimates and forecasts are essential to enable policymakers in the fields of politics, business and society to make rational and sound decisions. KOMA, a new macro-model, was recently developed to forecast the Swiss and international economies. Central banks and forecasting institutions often still use large macro-models. Macro-models’ ‘simple’ structure compared with other models enables them to interpret findings in a straightforward way. KOMA uses Bayesian estimation methods, which are tailored to these models. This makes forecasting uncertainty easier and more intuitive. In addition, it enables prior knowledge to be included gradually and more formally. The forecasting team also programmed an package in the computer language R that will soon be available. As part of these changes the reporting process was updated and expanded to include dynamic charts and tables (https://konjunkturprognose.kof.ethz.ch).
Model variety is constantly being expande
KOF’s range of models will be expanded to include a quantitative dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) model in the next few years. This project has two objectives. First, its existing forecasting infrastructure will be further improved and supplemented. And, second, the model will enable KOF to analyse medium- and long-term economic scenarios. Recent years have been characterised by shocks such as the pandemic, economic turmoil, geopolitical conflict and war.
It is crucial for any economy to be resilient to such events. In order to ensure that this is the case for Switzerland, a research team began to develop a state-of-the-art trade model. This model will help to inform the Swiss public and policymakers about the hypothetical impact of unprecedented scenarios such as climate shocks and new trade wars, which would be difficult to assess using the existing data alone.
Switzerland’s Federal Finance Administration (FFA) is keen to analyse its internal data and to use it in order to produce timely and consistent estimates and forecasts. For this purpose it requires proprietary tools and models that are gradually introduced. KOF is working closely with the FFA to develop these models. To this end, various mixed-frequency models, a large Bayesian vector autoregression (BVAR) model and a structural equation model have been developed and then implemented at the FFA. These methods are used for the FFA’s conditional forecasting in order to predict the country’s budget deficits among other things.
New partnerships for the Nowcasting Lab
It is important to have not just long-term forecasts, which capture structural changes in the economy and society, but also to make timely, short-term estimates and forecasts, which can identify and quantify economic turning-points at an early stage. One of these projects is KOF’s Nowcasting Lab, which is a real-time testing platform for forecasting current-quarter gross domestic product (GDP) in various countries by using prematurely available and higher-frequency data. These models are updated daily based on large quantities of data and are published online. A multi-frequency echo state network forecasting model was integrated on the platform. The Nowcasting Lab also works constantly to expand its collaborations. In 2023 it signed a letter of comfort with Switzerland’s State Secretariat for Economic Affairs (SECO) and entered into partnerships with researchers at the University of St Gallen and the University of Manchester.
Digital technology and innovation in the Swiss economy

Chat GPT gave a further boost to artificial intelligence (AI) and made it available to a broad user segment. Although AI has already been used for some time in research, it is also the subject of research projects. There are currently attempts to estimate the impact that regional AI research has on the respective industrial activity in the United States. This approach considers the role of geographical proximity and includes data on academic publications and industrial patents.
Investigation into the significance of research & development costs
Between 2000 and 2016 there was a sharp decline in the proportion of firms actively engaged in research and development (R&D) in Switzerland. In the Netherlands, by contrast, this percentage increased. Moreover, the two countries achieve similar productivity growth. An international cooperation project between KOF and the University of Amsterdam analysed potential reasons for these differing trends and their impact on productivity growth. A comparison between Switzerland and the Netherlands shows that, in Switzerland, R&D costs increasingly influenced whether firms conducted R&D.
In the Netherlands, on the other hand, R&D costs were only a minor consideration owing to the measures taken to support R&D there. In-depth analysis based on a structural equilibrium model shows, however, that reducing R&D costs is far less important for productivity growth than strengthening firms’ ability to innovate and increasing their capacity to absorb external knowledge (e.g. through R&D collaborations). R&D support measures should therefore focus on the last two factors mentioned.
Labour market monitoring and labour shortages throughout the Swiss economy

KOF is conducting a project entitled ‘What Workers Want: Determinants and Implications of Job Search Strategies on an Online Job Platform’ as part of the ‘Digital Transformation’ national research programme (NFP 77) under the auspices of the Swiss National Fund (SNF). A sub-project is investigating under what conditions unemployed jobseekers consider changing professions and under what conditions employers are willing to recruit such individuals changing professions. This project uses new kinds of online klick data from jobseekers and employers on a public recruitment platform. Having conducted their analysis, the researchers developed a new type of metric to measure the ‘proximity’ of two professions. This involves using text analysis tools to gauge to what extent the skills requested in job advertisements match the activities mentioned.
An experiment conducted on several Swiss online recruitment platforms as part of a further international NFP collaboration project is examining the question of how jobseekers react to information on the pay and fringe benefits offered by firms. The main point of interest here is to gain a better understanding of what importance jobseekers attach to fringe benefits such as working from home, a canteen, a creche or a company car compared with the level of pay.
Studies on the promotion of refugees and young women in the labour market and STEM degree programmes
The issue of labour shortages remains significant. Addressing this problem will require new approaches and rethinking existing barriers. One of these barriers is how to integrate refugees into the labour market. A study jointly conducted by researchers from KOF and the Immigration Policy Lab at ETH Zurich shows that restricting refugees’ employment opportunities reduces their likelihood of finding a job and even depresses their wages over the long term. This imposes considerable costs on both the refugees themselves and the countries receiving them.
Another project that examines the issue of promoting skills in science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM) addresses the shortage of labour at an early stage. The ‘Edumap’ project examines whether events aimed at promoting the study of STEM subjects – such as short presentations by speakers from STEM professions – may be an effective way of increasing the number of young people choosing to study STEM subjects at university.
This involved evaluating two large-scale series of events designed to promote the teaching of STEM subjects in Swiss secondary schools. These events were the ‘ETH unterwegs’ (ETH on the road) series organised by ETH Zurich and the ‘Tecdays’ run by the Swiss Academy of Engineering Sciences (SATW). The overall impact of 173 events held at 82 schools with over 80,000 pupils and more than 1,500 speakers was analysed. Evaluations using comprehensive administrative data on students’ choices show that both events have helped to increase the numbers of young people studying STEM subjects at Swiss universities (including ETH), and this is especially true of female students. KOF is now investigating what characteristics are typical of event speakers who are particularly successful representatives of STEM subjects
Publications
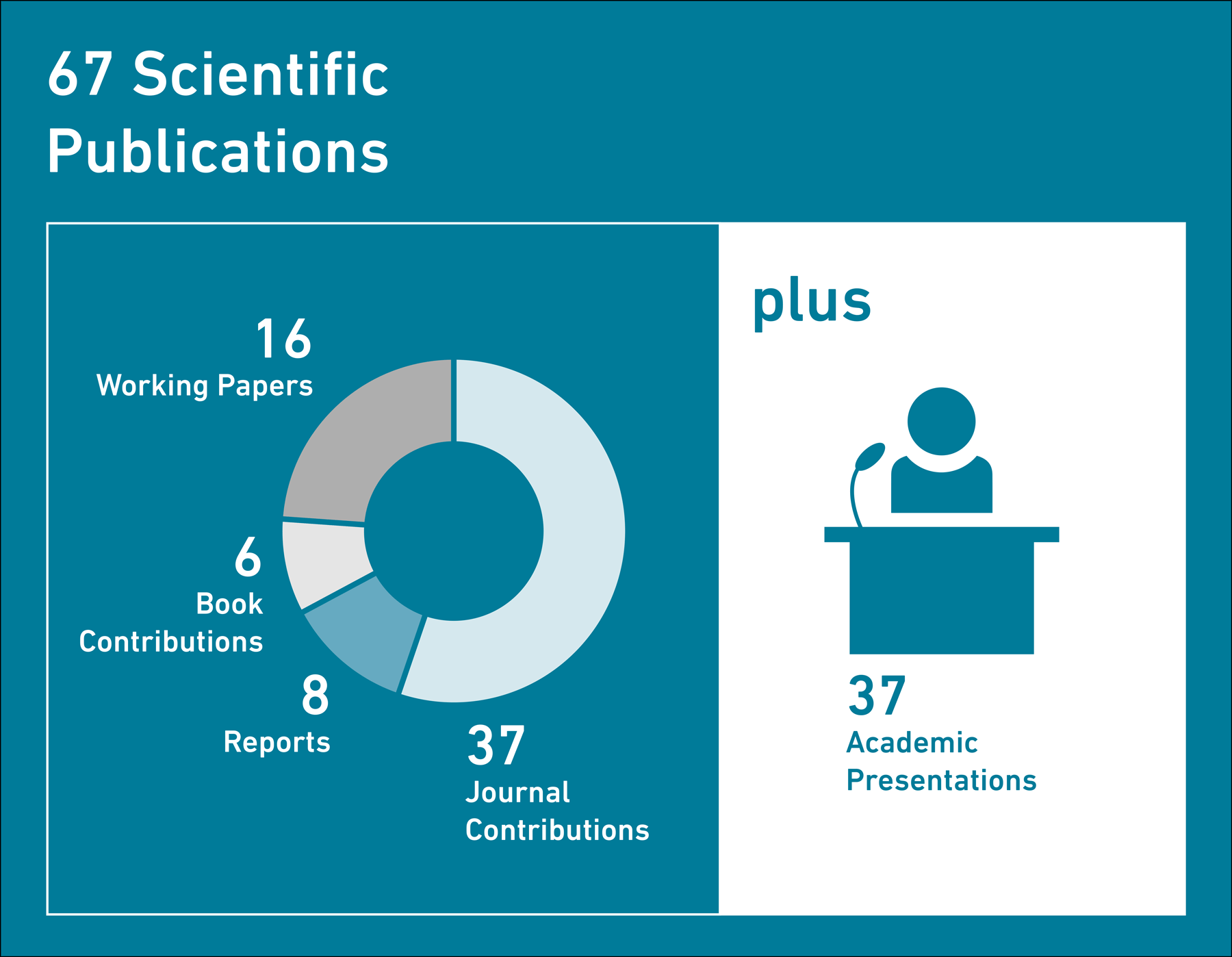
The publication of papers – especially in peer-reviewed journals – is an indicator of the quality of academic research. The researchers at KOF successfully published their empirical research in academic journals, KOF series and other prestigious working-papers series.
In 2023, a total of 37 articles were published by KOF employees in peer-reviewed journals, 12 more than in 2022. For example, an article entitled external page ‘Price setting on the two sides of the Atlantic – Evidence from supermarket scanner data’ by Pascal Seiler and his co-authors appeared in the Journal of Monetary Economics, while a paper entitled external page ‘Financial Intermediation, -Capital Accumulation, and Crisis Recovery’ by Hans Gersbach and his co-authors was published in the Review of Finance. Gersbach et al. published a further article entitled external page ‘Electoral Competition with Costly Policy Changes: A Dynamic Perspective’ in the Journal of Economic Theory. A study entitled external page ‘Closing the gender gap in academia? Evidence from an affirmative action program’ by Jan-Egbert Sturm and his co-authors appeared in the same category of journal (‘Research Policy’).
The European Economic Review simultaneously published two articles involving KOF researchers. The first was a paper entitled external page ‘Measuring macroeconomic uncertainty: A cross-country analysis’ by Samad Sarferaz and his co-author, while the second was an article by Michael König et. al. entitled external page ‘Endogenous technology cycles in dynamic R&D networks’. In addition, Martin Wörter and his co-authors published a paper entitled external page ‘In search of markets and technology: the role of cross-border knowledge for domestic productivity’ in ‘Industrial and Corporate Change’, while Michael Siegenthaler and his co-author published an article entitled external page ‘Train drain? Access to foreign workers and firms’ provision of training’ in the journal ‘Labour Economics’. Furthermore, some papers were accepted by prestigious journals such as the ‘American Economic Review’ and will be published over the next few years.
Further evidence of the quality of research is its acceptance at academic conferences. KOF researchers gave a total of 37 presentations at academic conferences in 2023, which was considerably more presentations than in 2022. Many conferences are now being held regularly again after having been suspended during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Prizes and awards
Mathias Beck won the 2023 Best Reviewer Award from the Industry and Innovation journal at the DRUID conference, which is one of the most prominent academic conferences in the field of innovation. This academic journal is one of the leaders in the areas of innovation and industry. Mathias Beck works in KOF’s Innovation Economics research division.
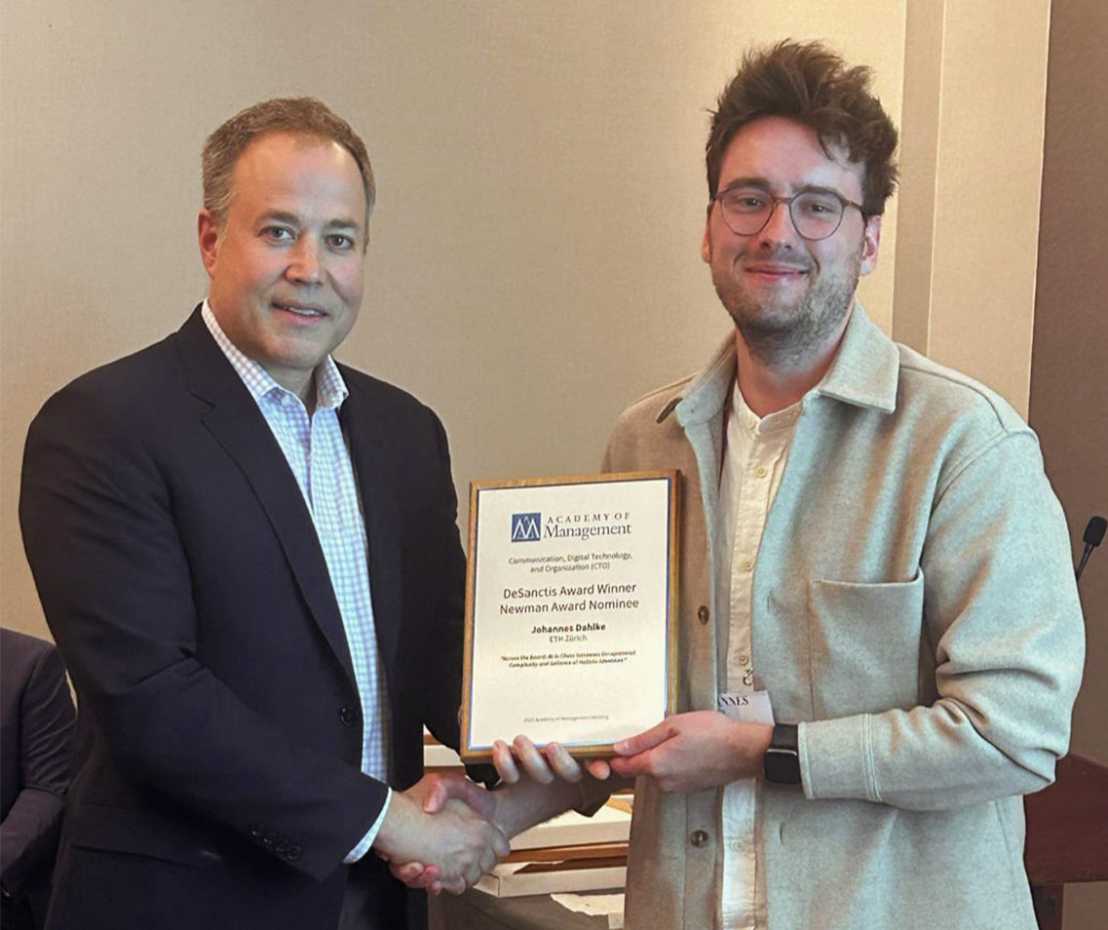

A further researcher from this field also received an award. Johannes Dahlke won the DeSanctis Award for his research (external page see paper) into the question of how AI technology has impacted on the knowledge work of professional chess grandmasters. As one of the first professions to engage in knowledge work, professional chess players perfectly illustrate what the latest research has predicted as a shift away from the substitution paradigm and towards a more interactive way of integrating AI technology into knowledge-intensive working environments. The DeSanctis Award was presented to Johannes Dahlke at the annual conference of the Academy of Management (AOM) in Boston. Numbering more than 10,000 attendees, this is the world’s largest and most prestigious conference in the field of management research.

Daniel Kopp, who works in the Swiss Labour Market research division, won the SIAF Award, which carries a prize of 10,000 Swiss francs, for his dissertation entitled external page ‘Essays on Recruitment and Layoffs in the Swiss Labor Market’. This prize, which is awarded by the Swiss Institute of International Studies (SIAF), is sponsored by the firm Ernst & Young AG. This accolade is conferred once a year on an outstanding PhD thesis from the University of Zurich or ETH Zurich for making an academic contribution to our understanding of political, economic, social and cultural relations in a globalised world.
In addition to winning a prize in 2023, Daniel Kopp became a Research Affiliate at the Institute for Labor Economics (IZA) in Bonn, Germany. Martin Wörter, who heads the Innovation Economics research division, was appointed a Research Associate at the ZEW – Leibniz Centre for European Economic Research in Mannheim, Germany.
Supporting young research staff

KOF attaches great importance to providing young economists with methodically rigorous training that focuses on empirical applications. 14.5 PhD students and four post-docs (in full-time equivalent [FTE] terms) were employed at KOF in 2023. This was 0.9 more (in FTEs) than in 2022. A total of four researchers successfully completed their doctorates last year. All of them remained at KOF in 2023. Overall, there was little fluctuation among the young scientists in 2023. Only Johannes Dahlke, a post-doc in the field of innovation economics, left KOF to take up a new position at a European university.

The dissertation submitted by Marc Anderes centred on an investigation of shocks. In this thesis he analysed different types of shocks, using various microeconomic and macroeconomic investigation methods, depending on the kind of shock being examined. His investigations cover a wide range of topcs and include real-estate demand shocks and their dynamic impact on macroeconomic components and households; estimates of a ‘true’ output gap; the effects of the European Central Bank’s (ECB) communication shocks on the direction of monetary policy and on experts’ expectations regarding key macroeconomic variables; and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic shock on the Swiss population’s mental health.

Sina Streicher’s dissertation examines macroeconomic dynamics as well as monetary and government policies in Europe In ihrer Dissertation beschäftigt sich Sina Streicher mit makroökonomischen Dynamiken und Geld- sowie Regierungspolitiken in Europa. She investigates the effects of the European Central Bank’s (ECB) communication on the direction of monetary policy and on experts’ expectations regarding key macroeconomic variables. She also estimates macroeconomic shocks at the level of European monetary union (EMU) and determines their impact on the member states and their production sectors. In addition, however, Streicher has developed the ‘RGAP’ R package, which enables potential output and the output gap to be estimated based on a production function approach proposed by the European Commission. She has also developed a multivariate Bayesian state-space model in order to determine potential output and the output gap consistent with the growth of the underlying production sectors as well as inflation and the labour market. Furthermore, Streicher examines the interaction between non-pharmaceutical containment measures, human behaviour and the spread of COVID-19 in Switzerland.

Philipp Baumann’s dissertation makes innovative contributions in the fields of macroeconometrics, statistics and machine learning in the form of five research articles. The first chapter uses the targeted maximum-likelihood estimate to investigate the effect that central bank independence has on inflation without finding compelling evidence for the hypothesis that it reduces inflation. The second chapter uses additive mixed models and boosting algorithms to analyse the determinants of inflation, with energy prices and demographic trends being identified as key factors. The third chapter introduces autoregressive transformation models (ATMs) for precise probabilistic time-series forecasts. The fourth chapter uses deep learning to estimate conditional transformation models, which enables a semi-parametric approach to be used to model the cumulative distribution function. The fifth chapter uses deep learning to expand the ATMs in order to improve the predictive power and interpretability of probabilistic forecasts. The dissertation emphasises the importance of suitable statistical and machine learning methods to meet the challenges posed by complex macroeconomic data.

Sebastian Heinrich’s dissertation examines various aspects of artificial intelligence (AI) from an economic perspective. Recent advances in computer algorithms, data availability and computing power have enabled machine learning and deep learning techniques to be widely applied across both industry and academia. Heinrich investigates this duality. First, he examines the spread of AI- and ICT-related knowledge and its broader economic effects. And, second, he analyses new approaches to developing indicators for the social and economic sciences in the wider sense using big data and machine learning techniques.
The seminar series regularly held at KOF provide PhD students and post-docs with the opportunity to present their work, discuss it and familiarise themselves with external researchers’ projects. This enables them to refine their own methods and learn about other fields of research within economics. In addition, KOF once again organised the Young Swiss Economists Meeting of the Swiss Society of Economics and Statistics in 2023. This conference provides an excellent opportunity for young economists to interact with other researchers from across Switzerland.
Visiting researchers
The exchange of ideas with other researchers from around the world is essential. An institute such as KOF, which is small by international standards, can only conduct many of its research projects because they are run as collaborations with researchers both in Switzerland and abroad. Visiting researchers in 2023 were external page Giovanni Ballarin from the University of Mannheim, external page Andreas Dibiasi from the Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, external page Vera Eichenauer from Germany’s Federal Ministry of Finance and KOF Research Fellow, Camilo Gómez Molina from Colombia’s central bank, external page Regina Pleninger from the World Bank and KOF Research Fellow, Johannes Rauch from the School of Business and Economics at the University of Amsterdam and external page Dan-Olof Roth from the Swedish Institute for Social Research (SOFI) at the University of Stockholm.
Pascal Seiler, a PhD student working in KOF’s Business Tendency Surveys research division, had the opportunity to deepen his research at the European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt. Michael König, a post-doc working in the Innovation Economics research division, was a visiting researcher at the Institute for New Economic Thinking at the University of Oxford, and KOF’s co-director Jan-Egbert Sturm was a visiting researcher at the University of Groningen.